Prenatal Yoga Teacher Training
Prenatal Yoga Teacher Training Course
- Home
- Prenatal Yoga Teacher Training
Basics of a Prenatal class
Before the class:
• Individual or group
• Aware of each student’s unique issues, stage of pregnancy, fitness level, etc.
• Beginner vs. advance practitioner
• Arrange for appropriate props-bolsters, straps, chair, wall, block, bench/stool, blankets, etc.
• Set expectations and counsel students prior to starting
General format of a Prenatal class
Usually students opt for a package of 5-8 classes, with written plans for self practice• Presencing, breath awareness
• Gentle warm up
• Modified Sun salutations as appropriate
• Asanas
• Pranayama
• Chanting (optional)
• Meditation (optional)
• Relaxation
Benefits of Pre and Post natal yoga
• Improves strength and endurance
• Balances the body and mind
• Calms the nervous system, improves sleep• Improves circulation
• Creates body and breath awareness, corrects postural issues, prevents aches and pains
• Helps prevent complications such as hypertension, gestational diabetes, swelling, etc
Benefits of Pre and Post natal yoga
• Improves strength and endurance
• Balances the body and mind
• Calms the nervous system, improves sleep• Improves circulation
• Creates body and breath awareness, corrects postural issues, prevents aches and pains
• Helps prevent complications such as hypertension, gestational diabetes, swelling, etc
Caution and Contraindications
• First trimester issues like fatigue and nausea may make asana practice challenging
• Women with medical complications (e.g. low fluid, prolapse) may be advised to avoid physical exercise
• Excessive discomfort or pain during practice requires medical investigation
MODULE 2: Anatomy and Physiology
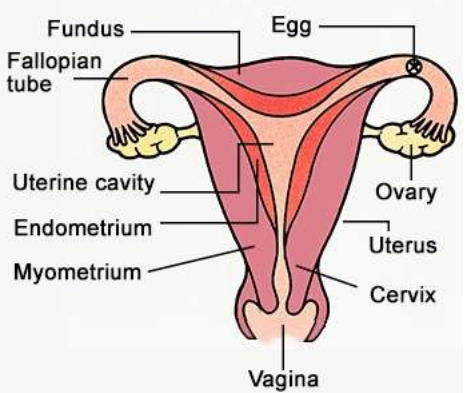
Female Reproductive System
• Ovaries: Glands that produce estrogen and progesterone as well as ova
• Fallopian tubes: Muscular tubes that transport fertilized egg to the uterus
• Uterus: Pear shaped muscular chamber
• Endometrium: Inner lining of the uterus
• Cervix: Entrance of the uterus• Vagina: muscular tube that connects the cervix to the exterior
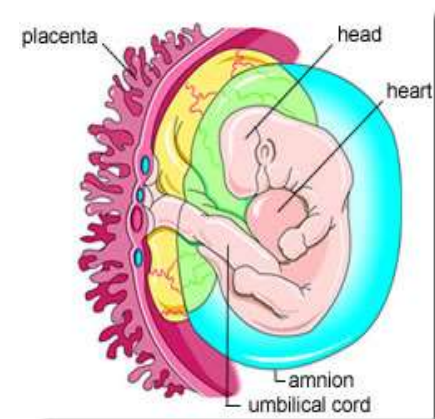
It all begins with an egg
• Ovulation: egg released from ovary
• Conception: Egg moves down the fallopian tube. If a sperm meets and enters the egg, fertilization occurs
• Implantation: Egg continues down and buries itself in the
endometrium within 7 days. Placenta begins to form
• HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) levels rise
• Embryo: for the first 8 weeks the fertilized egg is called an
embryo
• Fetus: 8 weeks till birth
Hormones during pregnancy
• HCG- nourishes the fetus, maintains corpus luteum and stimulates production of progesterone until about the 10th week
• Estrogen-increase in estrogen during pregnancy enables the uterus and placenta to improve vascularization, transfer nutrients, and support the developing baby. It plays an important role in helping the fetus develop and mature. Estrogen levels increase steadily during pregnancy and reach their peak in the third trimester. During the second trimester, estrogen plays a major role in the milk duct development that enlarges the breasts.
• Progesterone- increase in progesterone cause a laxity or loosening of ligaments and joints throughout the body. Builds immunity, allowing the mother to tolerate new DNA. In addition, high levels of progesterone cause internal structures to increase in size, especially the uterus.
• Oxytocin : stimulates the uterus to contract, cervix to expand, and stimulates the nipples to release milk.
• Prolactin: prepares the breast tissue for milk production. Has a tranquilizing effect.
• Relaxin: relaxes the pelvic joints in preparation for delivery.
First Trimester: the mother
• Lasts until about the 13th week.
• Rapid rise in estrogen and progesterone- nausea, fatigue, constipation, heartburn and frequent urination
• Tenderness and heaviness of breasts as the mammary glands start developing
• Dizziness due to dilated blood vessels and lower blood pressure
• Emotional ups and downs- anxiety, exhilaration, depression, etc.
• Medical tests include Rh screening, Hep B, HIV, chromosomal testing, ultrasound, amniocentesis, etc.
Possible Complications during the first trimester
• Miscarriage
• Ectopic Pregnancy- implantation outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube
• Excessive vomiting causing dehydration • High fever, vaginal discharge, severe headaches, swelling of legs must all be investigated
Second Trimester: the mother
• Usually the best time during pregnancy- weeks 14-27
• Hormones begin to even out
• Pregnancy “glow” sets in, lesser hairfall, cravings • Possible hyperpigmentation, linea nigra
• Possible leaking of colostrum
• Start to feel movements of fetus
• Medical tests include blood tests, ultrasound, fetal heartbeat, glucose tolerance, urine tests
Possible complications in 2nd trimester
• Premature labor
• Gestational diabetes
• Possible backache, hemarrhoids, heartburn, swelling of ankes and feet.
Third Trimester: the mother
• Significant increase in weight and girth
• Difficulty sleeping comfortably
• Increased pressure on the ribs
• Increase in breast size and fullness
• Preparation for delivery and the baby
Possible complications in the 3rd trimester
• Gaining too much weight
• Hypertension
• Breech position
• Premature rupture of membranes
Preparing for delivery
• Birth plan – doctor, hospital, method of delivery, pain control, procedures that may be needed
(episiotomy, forceps, vacuum)
• Support of partner/ family
• Post delivery discharge plan and support
